The price pressures that accompanied buoyant economic activity last year appear to have already peaked, but core inflation remains at persistently high levels, disproportionately hurting low-income households.

To mitigate the risk of inflation lock-in, fiscal policy can assist monetary policy in reducing demand pressures.
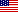
After peaking at 10% in mid-2022, headline inflation in the major Latin American economies has slowed to 7% in march.
But this decline is mainly due to the decline in commodity prices from their peak levels. Meanwhile, progress in reducing core inflation excluding food and energy appears to have stalled. Labor demand is very strong, and employment remains firmly above pre-pandemic levels.

At the same time, output is at or above potential, and near-term inflation expectations are above central banks' target ranges. Strong domestic demand, rapidly rising wages and widespread price pressures suggest the risk of inflation remaining at unacceptably high levels in the region.
Restoring price stability is fundamental to having a healthy economy and protecting the most vulnerable groups. At the current juncture, this means slowing domestic demand.

With inflation, especially core inflation, well above target and economies operating above their potential, policymakers no longer face the macroeconomic trade-off of late 2021 and early 2022, when fighting inflation was pitted against the need to support recovery from the pandemic.
The policy objective now must be to slow demand to bring it in line with potential output. This inevitably requires cooling the labor market.
Translated by: A.M
 English
English  Español
Español 
